
What policies are Organisations implementing to use the Cloud more securely?
Cloud computing remains an integral part of business today. The cloud gives you access to more applications, improves data accessibility, helps your team collaborate more effectively, and provides easier content management. The rise of malware and hacking techniques continues to threaten different organisations' data and IT resources on the cloud.
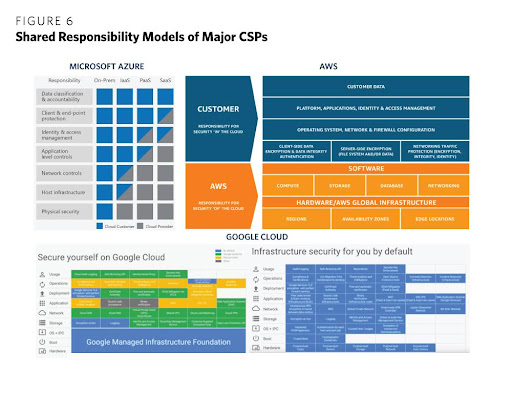
Before we look at some of the policies that organisations are implementing to secure their cloud, it is pertinent to talk about the Shared Responsibility Model.
Shared Responsibility Model
The Shared Responsibility Model, a security and compliance framework that outlines the responsibilities of cloud service providers (CSPs) and customers for securing every aspect of the cloud environment. You can learn more about the Shared Responsibility Model in our previous blog post. This framework dictates that you, the cloud user, be more accountable for the security and control of your own operating systems, applications, data and user access management running in the cloud, while your cloud provider is to be accountable for the security of the cloud infrastructure–hardware, software, networking and facilities that basically run the cloud.
When you do not take responsibility for your own part in the Shared Responsibility Model, there’s bound to be security breaches within your cloud security platform hence the need for cloud security policies that serve as a guide for an improved cloud security posture.
Gratner’s article, ‘Is the Cloud Secure?” predicts that through 2025, 90% of the organisations that fail to control public cloud use will inappropriately share sensitive data. Through 2024, the majority of enterprises will continue to struggle with appropriately measuring cloud security risks, and through 2025, 99% of cloud security failures will be the customer’s fault.
Cloud Security Policies
Cloud security policies are the guidelines under which companies operate in the cloud. They are often implemented in order to ensure the integrity and privacy of company-owned information. Having a cloud security policy is crucial for any company given the growing global popularity of cloud computing and the rise in data breaches and security threats. Companies should think about including the value of cloud security in their current security standards and policies. Cloud security policies must also be interchangeable and adaptable to comply with the ever changing threats to cloud resources..
The management team, security team, development team, and other teams within the company must all contribute to the cloud security policies that govern your company. All cloud security strategies, designs, and deployment are based on these policies. These policies give guidance on how the problems and threats should be solved in the best way possible.
Cloud Security Policies Being Adopted Globally
These policies are proven to improve the security posture of your cloud environment, and keep your cloud data safe; as well as grants the ability to respond to threats and challenges quickly and efficiently.
Some of these cloud security policies are:
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires authentication from multiple sources to verify a user’s identity. Without it, a user’s credentials can be stolen and used to access the cloud. This can be done through your IAM in your AWS Management console.
- Create Access Control Rules: Access control rules help protect cloud data from unauthorised access by allowing cloud administrators to set permissions for individual users and groups. These rules allow administrators to control who can access what data, as well as what they can do with it.
- Monitor User Activity: Regular monitoring of user activity can help detect potential security threats, such as suspicious logins or file access. Monitoring also allows administrators to identify any potential misconfigurations in the cloud environment that could lead to a security breach.
- Implement Encryption: Encryption is an important security measure that helps protect data in transit and at rest. By encrypting data, you can ensure that only authorised users can access your data, even if it is stolen or leaked. Cloud Security Posture Management tools can help you detect any security misconfigurations within your cloud environment.
- Use a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB): A CASB is a security solution that provides visibility and control over cloud applications. It helps organisations monitor, detect, and prevent malicious activity in their cloud environment.
- Cloud Security Posture Management SaaS tools: CSPMs are used to run daily, and real-time scans across your cloud assets, and detect any security misconfigurations that could lead to security breaches in your cloud environment. These SaaS tools assist your SecOps and DevSecOps or Cloud Security teams within your organisation.
Wendu and Cloud Security Policies
The cost of fixing a data breach far outweighs the price of proper precautions. A cloud security policy, therefore, provides you with the appropriate cautionary steps when operating on the cloud. This policy allows you to leverage the cloud’s benefits without taking on unnecessary risks.
These are some of the features on WENDU that implements the Cloud Security Policies:
- IAM Exposure: On the IAM dashboard, you get information on how many accounts within your team have disabled MFAs; and not just that, but which accounts are not adhering to the MFA policy within the team.
- Full Visibility Of Your Cloud Environment: On WENDU, you can get full visibility and monitoring of your cloud environment to identify areas for significant security improvements and optimisation.
- External Exposure: WENDU detects security misconfigurations, publicly exposed access keys, cloud asset exposure and more.
Learn more about Wendu here, and you can also request a demo to see Wendu in action.